Chem 2 Ap Homework Atomic Orbitals With Answers
ADVERTISEMENT
Chem 2 AP Homework #7-4: Problems pg. 299 #57, 58, 61, 62, 63, 67, 71, 77, 80, 83, 91, 124
57
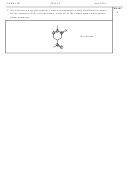
Discuss the similarities and differences between a 1s and a 2s orbital.
A 2s orbital is larger than a 1s orbital. Both have the same spherical shape. The 1s orbital is lower
in energy than the 2s.
58
What is the difference between a 2p
and a 2p
orbital?
x
y
The two orbitals are identical in size, shape, and energy. They differ only in their orientation with
respect to each other.
61
Calculate the total number of electrons that can occupy (a) one s orbital; (b) three p orbitals;
(c) five d orbitals; (d) seven f orbitals.
There can be a maximum of two electrons occupying one orbital.
(a) two
(b) six
(c) ten
(d) fourteen
The Pauli exclusion principle demands a maximum of two electrons per orbital. All orbitals of the
same type in the same energy level have the same energy and differ only in their orientation. All
sublevels of the same designation hold the same number of electrons.
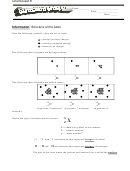
62
What is the total number of electrons that can be held in all orbitals having the same principal
quantum number n?
n value
orbital sum
total number of electrons
1
1
2
1 + 3 = 4
2
8
1 + 3 + 5 = 9
3
18
1 + 3 + 5 + 7 = 16
4
32
1 + 3 + 5 + 7 + 9 = 25
5
50
1 + 3 + 5 + 7 + 9 + 11 = 36
6
72
2
In each case the total number of orbitals is just the square of the n value (n
). The total number of
2
electrons is 2n
.
63
Determine the maximum number of electrons that can be found in each of the following
subshells: 3s, 3d, 4p, 4f, 5f.
The maximum number of electrons that can be found in the following subshells is:
3s: two
3d: ten
4p: six
4f: fourteen
5f: fourteen
67
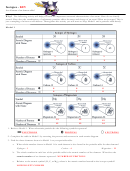
For each of the following pairs of hydrogen orbitals, indicate which is higher in energy: (a) 1s,
2s; (b) 2p, 3p; (c) 3d
, 3d
; d) 3s, 3d; (e) 4f, 5s.
xy
yx
In hydrogen, the energy does not depend on the orbital type, only on the principal quantum number
n. If two orbitals in the hydrogen atom have the same value of n, they have equal energy.
(a) 2s > 1s
(b) 3p > 2p
(c) 3d
= 3d
(d) 3s = 3d
(e) 5s > 4f
xy
yz
71
What is electron configuration? Describe the roles that the Pauli exclusion principle and
Hund’s rule play in writing the electron configuration of elements.
Electron configuration is the arrangement of electrons in the orbitals of an atom. The Pauli exclusion
principle allows a maximum of two electrons in any single orbital; Hund’s rule states that, when
filling orbitals of equal energy (degenerate), all orbitals are half filled before any orbital is
completely filled.
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2