Solubility Rules And Activity Of Metals Reference Sheet
ADVERTISEMENT
Supplemental Chemical Reactions 5-2
Solubility Rules and Activity of Metals Reference Sheet
Solubility Rules
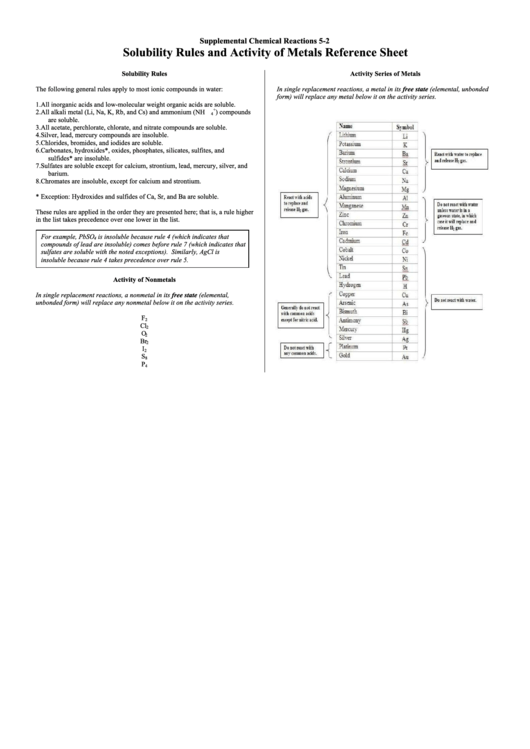
Activity Series of Metals
The following general rules apply to most ionic compounds in water:
In single replacement reactions, a metal in its free state (elemental, unbonded
form) will replace any metal below it on the activity series.
1.
All inorganic acids and low-molecular weight organic acids are soluble.
+
2.
All alkali metal (Li, Na, K, Rb, and Cs) and ammonium (NH
) compounds
4
are soluble.
3.
All acetate, perchlorate, chlorate, and nitrate compounds are soluble.
4.
Silver, lead, mercury compounds are insoluble.
5.
Chlorides, bromides, and iodides are soluble.
6.
Carbonates, hydroxides*, oxides, phosphates, silicates, sulfites, and
sulfides* are insoluble.
7.
Sulfates are soluble except for calcium, strontium, lead, mercury, silver, and
barium.
8.
Chromates are insoluble, except for calcium and strontium.
* Exception: Hydroxides and sulfides of Ca, Sr, and Ba are soluble.
These rules are applied in the order they are presented here; that is, a rule higher
in the list takes precedence over one lower in the list.
For example, PbSO
is insoluble because rule 4 (which indicates that
4
compounds of lead are insoluble) comes before rule 7 (which indicates that
sulfates are soluble with the noted exceptions). Similarly, AgCl is
insoluble because rule 4 takes precedence over rule 5.
Activity of Nonmetals
In single replacement reactions, a nonmetal in its free state (elemental,
unbonded form) will replace any nonmetal below it on the activity series.
F
2
Cl
2
O
2
Br
2
I
2
S
8
P
4
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1








