The Mental Status Examination Chart
ADVERTISEMENT
THE MENTAL STATUS EXAMINATION
Robert M. House M.D.
1. What is the mental status examination?
induced mania. The patient denied drug abuse. However,
questioning his wife uncovered a history of substance abuse,
and laboratory evaluation revealed the presence of
The mental status examination (MSE) is a component of all
amphetamine metabolites. The correct diagnosis was
medical exams and may be viewed as the psychological
amphetamine-induced mood disorder.
equivalent of the physical exam. It is especially important in
neurologic and psychiatric evaluations. The purpose is to
evaluate, quantitatively and qualitatively, a range of mental
3. What key factors should be considered along with the
functions and behaviors at a specific point in time. The MSE
MSE?
provides important information for diagnosis and for
assessment of the disorder’s course and response to
To assess properly the patient’s mental status, it is important
treatment. Observations noted throughout the interview
to have some understanding of the patient’s social, cultural,
become part of the MSE, which begins when the clinician
and educational background. What may be abnormal for
first meets the patient. Information is gathered about the
someone with more intellectual ability may be normal for
patient’s behaviors, thinking, and mood.
someone with less intellectual ability. Patients for whom
English is a second language may have difficulty
At an appropriate point in the evaluation the formal MSE is
understanding various components of the MSE, such as the
undertaken to compile specific data about the patient’s
proverbs. Age may be a factor. In general, patients over the
cognitive functioning. Earlier informal observations about
age of 60 years tend to do less well on the cognitive elements
mental state are woven together with the results of specific
of the MSE. Often this is related to less education rather than
testing. For example, the interviewer will have considerable
to aging alone.
information about attention span, memory, and organization
of thought from the process of the interview. Specific
4. What are the major components of the MSE?
questions during the formal exam clarify more precisely the
degree of attention or memory dysfunction.
Components vary somewhat from author to author. However,
most detailed MSEs include information about appearance,
Case.
motor activity, speech, affect, thought content, thought
process, perception, intellect, and insight.
A 55-year-old man presented with recent complaints of
sadness and fear of being alone. He also expressed thoughts
about death. As he presented his concerns, he rambled to
unrelated topics and seemed to lose track of the interviewer’s
questions. During the formal inquiry he was able to recall
only 1 of 3 objects he was asked to memorize and made
several mistakes in serial subtractions of 7 from 100. Specific
questioning about suicidal wishes and actions revealed that
he had overdosed with aspirin 1 month earlier and still
experienced suicidal thoughts and wishes to die. The
cognitive tests were compatible with mild dementia, and the
differential diagnosis included major depression. Further
work-up and treatment supported this diagnosis. Cognitive
functioning improved with antidepressants.
2. Is the MSE a separate part of the patient evaluation?
No. The MSE must be interpreted along with the presenting
history, physical exam, and laboratory and radiologic studies.
Separate interpretation makes you vulnerable to erroneous
conclusions. Collateral information from families and friends
is also invaluable to confirm or supply missing data.
Case.
A 27-year-old man presented to the psychiatric emergency
department with somewhat grandiose behavior, pressured
speech, irritability, and psychomotor agitation. The initial
diagnostic impression was bipolar disorder, manic or drug-
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Medical
 1
1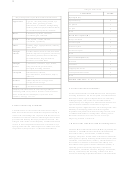 2
2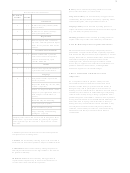 3
3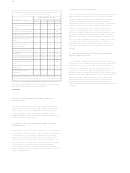 4
4








