Poly Atomic Ions Reference Sheet
ADVERTISEMENT
Chemistry: Poly Atomic Ions Notes
The prefix “poly” means many or much. Polyatomic ions are ions that are made up of more than one element.
Ironically, polyatomic ions are created when atoms of two or more elements are covalently bonded so that all of
the atoms have a full octet of valence electrons. However, in doing so they do not have an equal amount of
electrons and protons, therefore an ion is created instead of a neutral molecule.
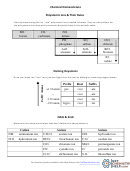
Examples of Neutral Compounds & Poly Atomic Ions
Combining Elements
Neutral Compound
Polyatomic Ion
-
Hydrogen and Oxygen
H
O (Water)
OH
(Hydroxide)
2
+
Nitrogen and Hydrogen
NH
(Ammonia)
NH
(Ammonium)
3
4
+
Nitrogen and Oxygen
NO
(Nitrogen Dioxide)
NO
(Nitrate)
2
3
2+
Sulfur and Oxygen
SO
(Sulfur Dioxide)
SO
(Sulfate)
2
4
Models of some Common Polyatomic Ions
+
-
-
2-
NH
(Ammonium)
OH
(Hydroxide)
NO
(Nitrate)
SO
(Sulfate)
4
3
4
Lewis Dot Structures
Determining the Charges of Polyatomic Ions
Each polyatomic ion has a charge just like a monoatomic ion has a charge. For example the ammonium ion has a
positive charge of 1 and the sulfate ion has a negative charge of 2. While it is relatively simple to predict the
charge of a monoatomic ion using the periodic table, it is more difficult to predict the charge of a polyatomic ion
using the periodic table. It’s best to use the charge sheet to memorize the names, formulas and charges of the
common polyatomic ions.
Ionic Compounds with Polyatomic Ions
Polyatomic ions are attracted to oppositely charged ions by the same electrostatic forces that attract monoatomic
ions to each other. Anions and cations combine in ratios that balance the charges to create neutral, ionic
compounds.
+
-
Examples: One Na
(sodium) ion combines with one OH
(hydroxide) ion to form NaOH (sodium hydroxide).
+
2-
Two H
(hydrogen) ions combine with one SO
(sulfate) ion to form H
SO
(sulfuric acid)
4
2
4
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1