Percents And Probability Worksheet With Answers - Lesson 12-19 Page 8
ADVERTISEMENT
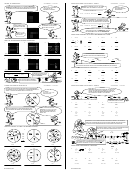
examPle 1
a. Find P(1 or 2) when rolling a number cube.
b. Find P(7) when rolling a number cube.
number of favorable outcomes (1, 2)
= 2 _
= 1 _
_______________________________
s
a. P(1 or 2) =
olutions
6
3
number of possible outcomes (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6)
It is somewhat likely a 1 or 2 will be rolled on a number cube.
number of favorable outcomes (7)
= 0 _
_______________________________
b. P(7) =
= 0
6
number of possible outcomes (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6)
It is impossible to roll a 7 on a number cube.
You can fi nd theoretical probability without actually rolling a number cube or fl ipping a coin. Th eoretical
probability is based on what should happen. Another type of probability is
experimental
probability. It is
based on what does happen aft er an experiment. Experimental probability is the ratio of the number of times
an event occurs to the total number of trials. Each trial is an individual experiment.
exPlOre!
cOin FliP
step 1: Copy the table below. Flip a coin 10 times.
a. Using tallies, record the number of times the coin lands on heads and the number of times
it lands on tails.
heads
tails
b. Determine your experimental probability of the coin landing on heads from 10 fl ips by
putting numbers in the following ratio. Write the probability as a fraction and a decimal.
number of heads
_______________
P(heads) =
total number of trials
step 2: Flip the coin 10 more times (now you have fl ipped the coin 20 times).
a. Add tallies to your chart for each additional head and tail.
b. Determine your experimental probability of the coin landing on heads with 20 fl ips
as you did in step 1b. Write the probability as a fraction and a decimal.
78
Lesson 13 ~ Probability
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26 27
27 28
28 29
29 30
30 31
31 32
32 33
33 34
34 35
35 36
36 37
37 38
38 39
39 40
40 41
41 42
42 43
43 44
44 45
45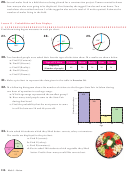 46
46 47
47 48
48 49
49