Similar Triangles, Right Triangles, And The Definition Of The Sine, Cosine And Tangent Functions Of Angles Of A Right Triangle Worksheets With Answer Key Page 8
ADVERTISEMENT
Figure T18 Two solutions
Figure T19 No solutions
Figure T20 One solution
Figure T21 One solution
Example: Solve ∆ABC where a = 10, c = 15 and A = 43°.
Solution: We attempt to solve for angle C by the Law of Sines:
15
10
=
°
sin
C
sin
43
so
⋅
°
15
sin
43
=
=
sin
C
. 1
023
.
10
There is no angle C for which sin C = 1.023. Hence, there is no triangle having these
sides and angles.
Example: Solve ∆ABC where a = 8.4, c = 10.5 and A = 53.13°.
Solution: By the Law of Sines,
⋅
°
10
5 .
8
4 .
10
5 .
sin
53
.
13
=
=
=
so
sin
C
. 1
000
(rounded).
sin
C
sin
53
.
13
8
4 .
Hence C = 90°. Thus, in this case there is exactly one solution. To complete the
solution, we find
=
°
−
+
=
°
−
°
=
°
B
180
(
A
C
)
180
(
143
.
13
)
36
.
87
.
Finally, solve for b by the Law of Sines:
°
b
10
5 .
10
5 .
sin
36
.
87
=
=
=
so
b
. 6
30
.
°
°
°
sin
36
.
87
sin
90
sin
90
- 8 -
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2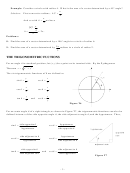 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6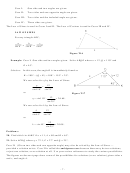 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13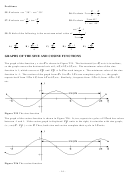 14
14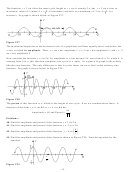 15
15 16
16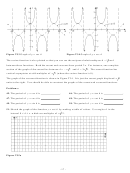 17
17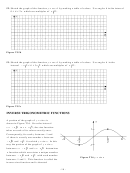 18
18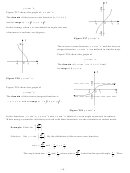 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26 27
27 28
28 29
29 30
30 31
31 32
32 33
33 34
34 35
35 36
36 37
37 38
38 39
39 40
40 41
41 42
42 43
43