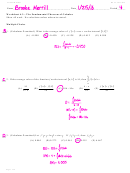
Heredity Worksheet With Answers Page 8
ADVERTISEMENT
Questions #33-36 refer to the following scenario:
In cats, one of the alleles responsible for coat color is located on the X chromosome. There are two
B
alleles for coat color, orange and black. Orange coat color (X
) is completely dominant to black coat color
b
(X
). However, there are tortoiseshell cats who have a mixture of black and orange fur. This occurs
because, in gametes with two X chromosomes, one X chromosome is randomly inactivated in each cell.
If the chromosome with a black allele is inactivated, that cell will display orange coloring, and vice versa.
This results in a mixture of coloring on these cats.
33. Upon first glance, a cat with a mixture of black and orange fur appears to follow what
dominance pattern?
a. Epistasis
b. Incomplete dominance
c. Codominance
d. Multiple alleles
34. What type of cats typically display the tortoiseshell coloring?
a. Males
b. Females
B
c. Homozygous X
b
d. Homozygous X
35. If a black male mates with an orange female, what percentage of the female offspring will be
tortoiseshell?
a. 25%
b. 50%
c. 75%
d. 100%
36. If an F
male from the cross in #35 is crossed with a tortoiseshell female, what percentage of the
1
offspring will be orange?
a. 25%
b. 50%
c. 75%
d. 100%
Questions #37-40 refer to the following scenario:
In pea plants, yellow seeds (Y) are dominant to green seed (y) and round seeds (R) are dominant to
wrinkled seeds (r).
37. In a YyRr x yyrr cross with 1,000 offspring, what are the expected phenotypic results?
a. 250 yellow round; 250 yellow wrinkled; 250 green wrinkled; 250 green round
b. 500 yellow round; 500 green wrinkled
c. 750 yellow round; 250 green wrinkled
d. 375 yellow round; 375 green wrinkled; 125 yellow wrinkled; 125 green round
AP Biology
Heredity
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11