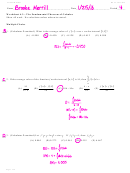
Heredity Worksheet With Answers Page 3
ADVERTISEMENT
Questions #13-14 refer to the following scenario:
In the primula plant, flower color is the result of epistasis. The pigment malvidin (M) creates blue
flowers. If this gene is homozygous recessive, the flower is not blue. Also, production of malvidin can be
suppressed if there is a dominant allele at gene D.
13. What does it mean for a phenotype to be the result of epistasis?
a. One gene controls more than one phenotype.
b. The phenotype is the result of unlinked genes.
c. More than one gene controls one phenotype.
d. The phenotype is the result of linked genes.
14. If two plants heterozygous for both genes are crossed, what will be the ratio of blue to nonblue
flowers?
a. 13 nonblue: 3 blue
b. 12 nonblue: 3 blue
c. 13 blue: 3 nonblue
d. 12 blue: 3 nonblue
15. What is the location of a sex-linked gene?
a. The X chromosome.
b. The Y chromosome.
c. Any autosome.
d. Either the X or Y chromosome.
16. Based on his experiments with pea plants, Mendel came up with a model for inheritance. Which
of the following is not part of his model?
a. Alleles are alternate versions of genes.
b. All gametes have two alleles for each genes.
c. One allele is dominant to the other.
d. Alleles separate from each other during gamete formation.
17. Recombination frequency applies to what type of genes?
a. Unlinked
b. Homeobox
c. Codominant
d. Linked
18. Pod color in pea plants can be either green or yellow, with green (G) being dominant to yellow
(g). What would be the alleles for the parental generation in a monohybrid cross for this trait?
a. Gg x Gg
b. GG x gg
c. GG x GG
d. gg x gg
AP Biology
Heredity
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11