Heredity Worksheet With Answers Page 10
ADVERTISEMENT
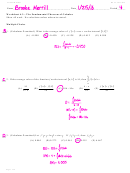
Quantitative Review – Heredity
1. Brown spots (B) are dominant over no spots (b). If a Bb individual is crossed with a BB individual
resulting in 200 offspring, how many offspring will be heterozygous for the trait?
2. In humans, having dimples (D) is dominant over not having dimples (d) and a cleft chin (C) is
dominant over a smooth chin (c). If a male and female heterozygous for both genes have
children, what percentage will have dimples and a smooth chin?
3. Colorblindness is a recessive x-linked trait. If a colorblind female has children with a normal
male, what percentage of their male children will be colorblind?
4. In humans, having a widow’s peak (W) is dominant to not having a widow’s peak (w). If a male
with genotype Ww has children with a female with genotype ww, what percentage of offspring
will not have a widow’s peak?
5. In pea plants, tall stems (T) are dominant to dwarf stems (t) and round seeds (R) are dominant
to wrinkled seeds (r). In a TtRr x ttrr F
cross that produces 500 F
plants, how many plants have
1
2
dwarf stems and round seeds?
6. In guinea pigs, white coat color (b) is recessive to black coat color (B). If two heterozygotes are
crossed, what percentage of offspring will also be heterozygous?
7. White eyes in fruit flies is a recessive x-linked trait. If a carrier female is crossed with a wild type
male, resulting in 742 female and 760 male offspring, how many of the males will have white
eyes?
8. In a AaBbCc x AaBbcc cross, what percentage of offspring are homozygous recessive for all
traits?
AP Biology
Heredity
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11