1.3 Maximum Or Minimum Of A Quadratic Function Worksheet - Mcgraw-Hill Education Canada Page 5
ADVERTISEMENT
Method 2: Use Partial Factoring to Determine the Vertex
Find the x-coordinate of the vertex of the function Q(x) 5 2x
4x,
2
knowing that the vertex of P(x) 5 2x
4x 160 has the same
2
x-coordinate.
Q(x) 5 2x(x 2)
Substitute Q(x) 5 0 to find the x-intercepts.
0
5 2x(x 2)
2x 5 0 or x 2 5 0
x 5 0 or
x 5 2
The x-coordinate of the vertex is x 5 1 (the average of 0 and 2).
P(1) 5 2(1)
4(1) 160
2
5 162
The vertex of this function is at (1, 162). This means that they will make
a maximum profit of $162 if they increase the price once. The selling
price is 10 0.5(1) or $10.50.
example 4
Connect Projectiles to Quadratic Functions
Jamie throws a ball that will move through the air in a parabolic path due
Co nne c tio ns
to gravity. The height, h, in metres, of the ball above the ground after
The zeros of a function
t seconds can be modelled by the function h(t) = 4.9t
40t 1.5.
2
are the values of the
Find the zeros of the function and interpret their meaning.
a)
independent variable
for which the function
has value zero. They
b)
Determine the time needed for the ball to reach its maximum height.
correspond to the
x-intercepts of the
c)
What is the maximum height of the ball?
graph of the function.
Solution
a)
• Use the window settings shown.
• Graph Y1 5 4.9x
40x 1.5.
2
• Press
[CALC] to access the CALCULATE
2nd
menu.
1.3 Maximum or Minimum of a Quadratic Function • MHR 9
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5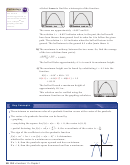 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9