Quadratics In Vertex Form Worksheet Page 3
ADVERTISEMENT
Get the Gizmo ready:
Activity B:
Set a to 1.0, h to 1.0, and k to –4.0.
Turn on Show vertex and intercept(s).
The intercepts
Turn off Show axis of symmetry.
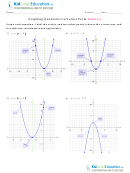
1. The function graphed in the Gizmo should be y = (x – 1)
2
– 4.
A. The y-intercept of the graph is the value of y when x
is zero. Write an equation for the y-intercept of this
graph. Then simplify the equation in the space to the
right. Check your answer by comparing it to the
y-intercept given in the Gizmo.
B. Now simplify the right side of the equation y = a(0 – h)
2
+ k. What is the general
equation of the y-intercept? y =
Experiment with a variety
of quadratic functions to check that this equation always works.
2. Graph the function y = (x – 1)
2
– 4 again.
A. The x-intercepts of the graph are the values of x
when y is zero. Substitute zero for y in y = (x – 1)
2
– 4
and solve for x. Show your work in the space to the
right. Check your answer by comparing it to the
x-intercepts given in the Gizmo.
B. Turn on Show axis of symmetry to see the axis of symmetry. How do the locations
of the x-intercepts of this graph relate to the axis of symmetry?
Vary the value of k to check that this relationship always exists.
C. Solve the equation 0 = a(x – h)
2
+ k for x to
find the general equation of the x-intercepts.
Show your work in the space to the right.
(Remember that square roots can be
positive or negative.)
D. How does the general equation prove that the x-intercepts are equidistant from the
axis of symmetry? (Hint: Recall that the equation for the axis of symmetry is x = h).
(Activity B continued on next page)
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4