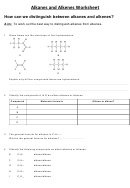
Alkanes And Cycloalkanes Worksheet Page 2
ADVERTISEMENT
2
b. Non-systematic names (isopropyl, sec-butyl, isobutyl, tert-butyl)
III. PROPERTIES OF ALKANES
1. Alkane reactivity (low) - what main reactions?
2. Trends in melting and boiling points
IV. CYCLOALKANES (ALICYCLIC COMPOUNDS)
1. Nomenclature
2. Cis-Trans isomerism (constitutional isomers vs. stereoisomers)
Chapter 3 Worksheet
What is a functional group?
How does the size and shape of a molecule effect the reactivity of its functional groups?
What are the functional groups which contain carbon-carbon multiple bonds?
What are the functional groups which contain carbon single bonded to an electronegative atom?
What are the functional groups with carbon double bonded to oxygen?
What are the alkanes?
Why are they called saturated hydrocarbons?
What is the difference between a branched-chain and a straight-chained alkane?
Define the term "isomer". What is a constitutional isomer? A stereoisomer?
What is a condensed structure?
How are the straight-chained alkanes named?
What is an alkyl group?
What do the names primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary (alkyl groups) signify?
How does the boiling point of an alkane vary with its structure?
What is the most important force when considering the intermolecular interactions between non-
polar molecules?
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3