Hardness Of Water By Edta Titration Worksheet
ADVERTISEMENT
Chemistry 201 Laboratory
Page 1 of 3
EXPERIMENT 1: HARDNESS OF WATER BY EDTA TITRATION
INTRODUCTION
Water ‘hardness’ is a measure of the amount of hard water cations in water. These hard
water cations include calcium, magnesium, iron, zinc and the other polyvalent metal ions.
In most water samples, calcium and magnesium are the chief contributors to water
hardness.
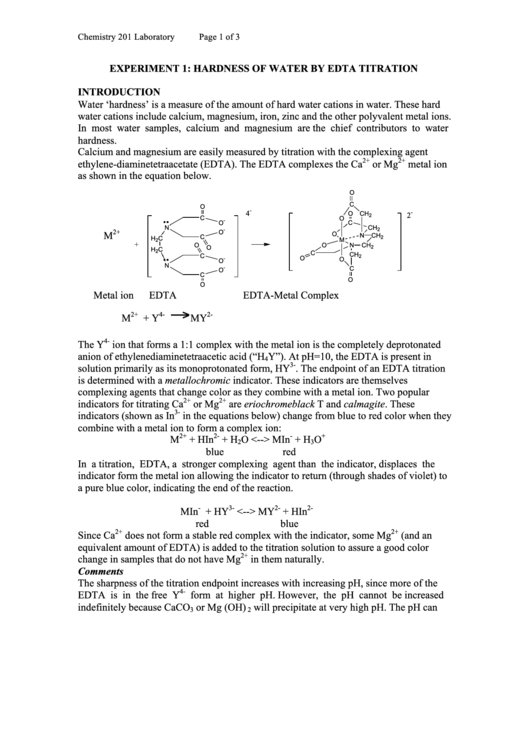
Calcium and magnesium are easily measured by titration with the complexing agent
2+
2+
ethylene-diaminetetraacetate (EDTA). The EDTA complexes the Ca
or Mg
metal ion
as shown in the equation below.
O
C
O
-
4
-
O
CH
2
2
C
O
-
O
C
N
CH
2
-
2+
O
M
O
N
CH
C
2
H
C
M
2
+
O
O
N
CH
O
2
H
C
2
C
CH
C
2
O
-
O
O
N
-
C
O
C
O
O
Metal ion
EDTA
EDTA-Metal Complex
→
2+
4-
2-
M
+ Y
MY
4-
The Y
ion that forms a 1:1 complex with the metal ion is the completely deprotonated
anion of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (“H
Y”). At pH=10, the EDTA is present in
4
3-
solution primarily as its monoprotonated form, HY
. The endpoint of an EDTA titration
is determined with a metallochromic indicator. These indicators are themselves
complexing agents that change color as they combine with a metal ion. Two popular
2+
2+
indicators for titrating Ca
or Mg
are eriochrome black T and calmagite. These
3-
indicators (shown as In
in the equations below) change from blue to red color when they
combine with a metal ion to form a complex ion:
2+
2-
-
+
M
+ HIn
+ H
O <--> MIn
+ H
O
2
3
blue
red
In a titration, EDTA, a stronger complexing agent than the indicator, displaces the
indicator form the metal ion allowing the indicator to return (through shades of violet) to
a pure blue color, indicating the end of the reaction.
-
3-
2-
2-
MIn
+ HY
<--> MY
+ HIn
red
blue
2+
2+
Since Ca
does not form a stable red complex with the indicator, some Mg
(and an
equivalent amount of EDTA) is added to the titration solution to assure a good color
2+
change in samples that do not have Mg
in them naturally.
Comments
The sharpness of the titration endpoint increases with increasing pH, since more of the
4-
EDTA is in the free Y
form at higher pH. However, the pH cannot be increased
indefinitely because CaCO
or Mg (OH)
will precipitate at very high pH. The pH can
3
2
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3








