Early Childhood Program Participation, From The National Household Education Surveys Program Of 2012 - U.s. Department Of Education Page 32
ADVERTISEMENT
Because ECPP-eligible children comprise a smaller portion of the population than the
kindergarten through grade 12 children who are eligible for the PFI, differential sampling in
households with children in both domains was applied to ensure a sufficient sample size for the
ECPP survey. The differential probabilities of selection (for households overall and within
households) are accounted for in the NHES weighting methodology. The ECPP sample is
nationally representative of all noninstitutionalized children in the 50 states and the District of
1
Columbia between birth and the age of 6.
The respondent to the ECPP questionnaire was a parent or guardian in the household who knew
about the sampled child. The respondent was asked detailed questions about the sampled child’s
current nonparental care arrangements, finding and choosing care for the child, family activities,
and things the child may be learning. The respondent was also asked basic demographic
questions about the child, as well as questions about the child’s health and disability status,
parent/guardian characteristics, and household characteristics. Multiple follow-up attempts were
made to obtain completed questionnaires from respondents who did not respond to the first
questionnaire that was mailed to them. The survey questionnaires were printed in both English
and Spanish. The total number of ECPP cases used in this report was 7,892, representing a
population of 21.7 million children when weighted to reflect national totals.
Data Reliability
Estimates produced using data from the NHES are subject to two types of errors: sampling errors
and nonsampling errors. Nonsampling errors are errors made in the collection and processing of
data. Sampling errors occur because the data are collected from a sample, rather than a census, of
the population.
Nonsampling Errors
Nonsampling error is the term used to describe variations in the estimates that may be caused by
population coverage limitations and data collection, processing, and reporting procedures. The
sources of nonsampling errors are typically problems such as unit and item nonresponse, the
differences in respondents’ interpretations of the meaning of survey questions, response
differences related to the particular month or time of the year when the survey was conducted,
the tendency for respondents to give socially desirable responses, and mistakes in data
preparation.
In general, it is difficult to identify and estimate either the amount of nonsampling error or the
bias caused by this error. For each NHES survey, efforts are made to prevent such errors from
occurring and to compensate for them, where possible. For instance, during the survey design
phase, cognitive interviews are conducted to assess respondents’ knowledge of the survey topics,
their comprehension of questions and terms, and the sensitivity of items.
1
The ECPP sample represents children who are age 6 but not yet in kindergarten; however, the tables in this report
are for children birth to age 5 because there are not enough children who are age 6 and not yet in kindergarten in
the final NHES data to support stable estimates.
22
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Legal
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20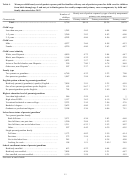 21
21 22
22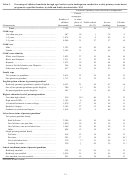 23
23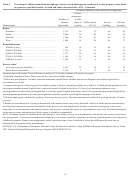 24
24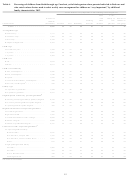 25
25 26
26 27
27 28
28 29
29 30
30 31
31 32
32 33
33 34
34 35
35 36
36 37
37 38
38 39
39 40
40 41
41 42
42 43
43 44
44 45
45 46
46 47
47 48
48 49
49 50
50 51
51 52
52 53
53 54
54 55
55 56
56 57
57 58
58 59
59








