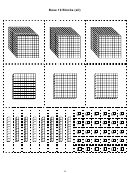
Model Decimals With Base-10 Blocks Page 3
ADVERTISEMENT
Student Page
Date
Time
2.
Hold up a flat in one hand and a long in the other. If this (the
LESSON
Place Value in Decimals
5 7
1 _
flat) is ONE, then what is this? (Hold up the long.)
10
3.
Write 0.1 on the board. Explain that this is another way of
1 _
writing
; 0.1 is read as one-tenth. Next to 0.1 write
10
1 _
one-tenth and
.
10
4.
Write 0.2 on the board. Partners show this number on their
grids with base-10 blocks. Place two longs on the grid. How
do you read this decimal?
Two-tenths
Next to 0.2, write
2 _
two-tenths and
. Repeat with other tenths, such as 0.3 and 0.4.
10
If the grid is ONE, then which part of each grid is shaded?
Write a fraction and a decimal below each grid.
1.
2.
3.
cube
long
flat
big cube
1
5
5
0
7
2
8
or
or
2
1
0
1
0
0
1
0
0
1
00
fraction:
fraction:
fraction:
0.5 or
0.08
0.72
decimal:
decimal:
decimal:
0.50
ONE
10
100
1,000
Math Journal 1, p. 114
1
0.1
one-tenth
—
10
2
0.2
two-tenths
—
10
0.01
0.1
ONE
10
3
0.3
three-tenths
—
10
4
0. 4
four-tenths
—
10
The value of the base-10 blocks depends on which block is ONE.
Ongoing Assessment: Informing Instruction
Teaching Aid Master
Watch for children who are having difficulty understanding that the value of
base-10 blocks can change. Explain that base-10 blocks model numbers, but
Name
Date
Time
A Flat
their values can change depending on which block is defined as the ONE. For
decimals, it’s often better to define the flat as the ONE.
Exploring Hundredths Using
WHOLE-CLASS
ACTIVITY
Base-10 Blocks
(Math Journal 1, p. 114)
Go through the following procedure with the class:
1.
Children place a single cube in a corner along the inside edge
of the grid on journal page 114. Ask: How many cubes do you
need to cover the whole grid?
100
What fraction of the grid is
1
_
one cube?
100
2.
Hold up a flat in one hand and a cube in the other. If this (the
1
_
flat) is ONE, then what is this? (Hold up the cube.)
100
Math Masters, p. 425
354
Unit 5 Place Value in Whole Numbers and Decimals
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2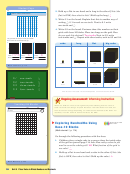 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7