Publication 54 - Tax Guide For U.s. Citizens And U.s. Citizens Abroad - 2001 Page 32
ADVERTISEMENT
of which is your foreign earned income. Enter
In this situation (Example 2), you can-
tive share of the partnership net profit, on
TIP
not use Form 2555 – EZ since you had
Schedule E (Form 1040). On Form 2555, show
the amount of the deduction(s) related to ex-
self-employment income and business
$78,000 on line 40 and show $31,200 on line 42.
cluded income on line 42 of Form 2555.
expenses.
Your exclusion on Form 2555 is $46,800.
If you have itemized deductions related to
excluded income, enter on Schedule A (Form
In this situation (Example 5), you would
TIP
Example 3. Assume in Example 2, that both
not use Form 2555 – EZ since you had
1040) only the part not related to excluded in-
capital and personal services combine to pro-
earned income other than salaries and
come. You figure that amount by subtracting
duce the business income. No more than 30% of
wages and you had business expenses.
from the deduction the amount related to ex-
your net income, or $12,000, assuming that this
cluded income. Generally, you figure the
amount is a reasonable allowance for your ser-
amount that is related to the excluded income by
vices, is considered earned and can be ex-
multiplying the deduction by a fraction, the nu-
cluded. Your exclusion of $12,000 is 12% of
merator of which is your foreign earned income
your gross income ($12,000/$100,000). Be-
exclusion and the denominator of which is your
cause you excluded 12% of your total income,
foreign earned income. Attach a statement to
6.
$7,200, or 12% of your business expenses, are
your return showing how you figured the deduct-
attributable to the excluded income and are not
ible amount.
deductible.
Example 1. You are a U.S. citizen em-
Example 4. You are a U.S. citizen, have a
Tax Treaty
ployed as an accountant. Your tax home is in
tax home in Brazil, and meet the physical pres-
Germany for the entire tax year. You meet the
ence test. You are self-employed and both capi-
physical presence test. Your foreign earned in-
Benefits
tal and personal services combine to produce
come for the year was $100,000 and your in-
business income. Your gross income was
vestment income was $12,000. After excluding
$146,000, business expenses were $172,000,
$78,000, your AGI is $34,000.
and your net loss was $26,000. A reasonable
Topics
allowance for the services you performed for the
You had unreimbursed business expenses
business is $77,000. Because you incurred a
This chapter discusses:
of $1,500 for travel and entertainment in earning
net loss, the earned income limit of 30% of your
your foreign income, of which $500 were for
•
net profit does not apply. The $77,000 is foreign
Some common tax treaty benefits,
meals and entertainment. These expenses are
earned income. If you choose to exclude the
•
deductible only as miscellaneous deductions on
How to get help in certain situations, and
$77,000, you exclude 52.74% of your gross in-
Schedule A (Form 1040). You also have $500 of
•
come ($77,000/$146,000), and 52.74% of your
How to get copies of tax treaties.
miscellaneous expenses that are not related to
business expenses ($90,712) are attributable to
your foreign income that you enter on line 22 of
that income and not deductible. Show your total
Schedule A.
Useful Items
income and expenses on Schedule C (Form
You must fill out Form 2106. On that form,
You may want to see:
1040). On Form 2555, exclude $77,000 and
reduce your deductible meal and entertainment
show $90,712 on line 42. Subtract line 42 from
expenses by 50% ($250). You must reduce the
Publication
line 41, and enter the difference as a negative (in
remaining $1,250 of travel and entertainment
parentheses) on line 43. Because this amount is
597
Information on the United
expenses by 78% ($975) because you excluded
negative, enter it as a positive (no parentheses)
States – Canada Income Tax
78% ($78,000/$100,000) of your foreign earned
on line 21, Form 1040, and combine it with your
Treaty
other income to arrive at total income on line 22
income. You carry the remaining total of $275 to
of Form 1040.
line 20 of Schedule A. Add the $275 to the $500
901
U.S. Tax Treaties
that you have on line 22 and enter the total
In this situation (Example 4), you would
See chapter 7 for information about getting
($775) on line 23.
TIP
probably not want to choose the for-
these publications.
On line 25 of Schedule A, enter $680, which
eign earned income exclusion if this
was the first year you were eligible. If you had
is 2% of your adjusted gross income of $34,000
chosen the exclusion in an earlier year, you
(line 34, Form 1040) and subtract it from the
might want to revoke the choice for this year. To
amount on line 23.
Purpose of Tax
do so would mean that you could not claim the
Enter $95 on line 26 of Schedule A.
exclusion again for the next 5 tax years without
Treaties
IRS approval. See Choosing the Exclusion, in
Example 2. You are a U.S. citizen, have a
chapter 4.
tax home in France, and meet the physical pres-
The United States has tax treaties or conven-
ence test. You are self-employed and personal
tions with many countries. Under these treaties
Example 5. You are a U.S. citizen, have a
services produce the business income. Your
and conventions, citizens and residents of the
tax home in Venezuela, and meet the bona fide
gross income was $100,000, business ex-
United States who are subject to taxes imposed
residence test. You have been performing ser-
penses $60,000, and net income (profit)
by the foreign countries are entitled to certain
vices for clients as a partner in a firm that pro-
$40,000. You choose the foreign earned income
credits, deductions, exemptions, and reductions
vides services exclusively in Venezuela. Capital
exclusion and exclude $78,000 of your gross
in the rate of taxes of those foreign countries. If a
investment is not material in producing the
income. Since your excluded income is 78% of
foreign country with which the United States has
partnership’s income. Under the terms of the
your total income, 78% of your business ex-
a treaty imposes a tax on you, you may be
partnership agreement, you are to receive 50%
penses are not deductible. Report your total
entitled to benefits under the treaty. See Table
of the net profits. The partnership received gross
income and expenses on Schedule C (Form
6 – 1, later.
income of $200,000 and incurred operating ex-
1040). On Form 2555 you will show the follow-
Treaty benefits generally are available to re-
penses of $80,000. Of the net profits of
ing:
sidents of the United States. They generally are
$120,000, you received $60,000 as your distrib-
not available to U.S. citizens who do not reside
utive share.
1) Line 20a, $100,000, gross income
in the United States. However, certain treaty
You choose to exclude $78,000 of your
benefits and safeguards, such as the nondis-
2) Lines 40 and 41, $78,000, foreign earned
share of the gross income. Because you ex-
crimination provisions, are available to U.S. citi-
income exclusion
clude 78% ($78,000/$100,000) of your share of
zens residing in the treaty countries. U.S.
3) Line 42, $46,800 (78% × $60,000) busi-
the gross income, you cannot deduct $31,200,
citizens residing in a foreign country may also be
ness expenses attributable to the exclu-
78% of your share of the operating expenses
entitled to benefits under that country’s tax trea-
(78% × $40,000). Report $60,000, your distribu-
sion.
ties with third countries.
Page 32
Chapter 6 Tax Treaty Benefits
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Financial
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11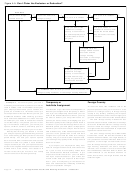 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26 27
27 28
28 29
29 30
30 31
31 32
32 33
33 34
34 35
35 36
36 37
37 38
38 39
39 40
40 41
41 42
42 43
43 44
44








