Publication 54 - Tax Guide For U.s. Citizens And U.s. Citizens Abroad - 2001 Page 11
ADVERTISEMENT
Form (and Instructions)
If you are a nonresident alien married to a
U.S. citizen or resident, and both you and your
Exemption From
1040X
Amended U.S. Individual Income
spouse choose to treat you as a resident, you
Tax Return
are a resident alien for tax purposes. For infor-
Social Security and
mation on making the choice, see the discussion
2555
Foreign Earned Income
Medicare Taxes
in chapter 1 under Nonresident Spouse Treated
2555 – EZ
Foreign Earned Income
as a Resident.
Exclusion
The United States may reach agreements with
Waiver of minimum time requirements. The
foreign countries to eliminate dual coverage and
See chapter 7 for information about getting
minimum time requirements for bona fide resi-
dual contributions (taxes) to social security sys-
these publications and forms.
dence and physical presence can be waived if
tems for the same work. See Binational Social
you must leave a foreign country because of
Security (Totalization) Agreements in chapter 2
war, civil unrest, or similar adverse conditions in
under Social Security and Medicare Taxes. As a
that country. This is fully explained at Waiver of
Who Qualifies for the
general rule, self-employed persons who are
Time Requirements under Exceptions to Tests,
subject to dual taxation will only be covered by
later.
Exclusions and the
the social security system of the country where
they reside. For more information on how any
Tax Home in
Deduction?
specific agreement affects self-employed per-
Foreign Country
sons, contact the United States Social Security
If you meet certain requirements, you may qual-
Administration, as discussed in chapter 2.
To qualify for the foreign earned income exclu-
ify for the foreign earned income and foreign
If your self-employment earnings should be
sion, the foreign housing exclusion, or the for-
housing exclusions and the foreign housing de-
exempt from foreign social security tax and sub-
eign housing deduction, your tax home must be
duction.
ject only to U.S. self-employment tax, you
in a foreign country throughout your period of
If you are a U.S. citizen or a resident alien of
should request a certificate of coverage from the
bona fide residence or physical presence
the United States and you live abroad, you are
abroad. Bona fide residence and physical pres-
U. S. Social Security Administration, Office of
taxed on your worldwide income. However, you
ence are explained later.
International Programs. The certificate will es-
may qualify to exclude from income up to
tablish your exemption from the foreign social
$78,000 of your foreign earnings. In addition,
security tax.
you can exclude or deduct certain foreign hous-
Tax Home
ing amounts. See Foreign Earned Income Ex-
Your tax home is the general area of your main
clusion and Foreign Housing Exclusion and
place of business, employment, or post of duty,
Deduction, later.
regardless of where you maintain your family
You may also be entitled to exclude from
home. Your tax home is the place where you are
income the value of meals and lodging provided
4.
permanently or indefinitely engaged to work as
to you by your employer. See Exclusion of Meals
an employee or self-employed individual. Hav-
and Lodging, later.
ing a “tax home” in a given location does not
necessarily mean that the given location is your
residence or domicile for tax purposes.
Foreign Earned
Requirements
If you do not have a regular or main place of
business because of the nature of your work,
Income and
your tax home may be the place where you
To claim the foreign earned income exclusion,
regularly live. If you have neither a regular or
the foreign housing exclusion, or the foreign
main place of business nor a place where you
Housing:
housing deduction, you must satisfy all three of
regularly live, you are considered an itinerant
the following requirements.
and your tax home is wherever you work.
Exclusion –
You are not considered to have a tax home in
1) Your tax home must be in a foreign coun-
a foreign country for any period in which your
try.
abode is in the United States. However, your
Deduction
2) You must have foreign earned income.
abode is not necessarily in the United States
while you are temporarily in the United States.
3) You must be either:
Your abode is also not necessarily in the United
•
States merely because you maintain a dwelling
A U.S. citizen who is a bona fide resident
Topics
in the United States, whether or not your spouse
of a foreign country or countries for an
This chapter discusses:
or dependents use the dwelling.
uninterrupted period that includes an en-
tire tax year,
“Abode” has been variously defined as one’s
•
Who qualifies for the foreign earned in-
•
home, habitation, residence, domicile, or place
A U.S resident alien who is a citizen or
come exclusion, the foreign housing exclu-
of dwelling. It does not mean your principal place
national of a country with which the United
sion, and the foreign housing deduction,
of business. “Abode” has a domestic rather than
States has an income tax treaty in effect
•
a vocational meaning and does not mean the
How to figure the foreign earned income
and who is a bona fide resident of a for-
same as “tax home.” The location of your abode
exclusion, and
eign country or countries for an uninter-
often will depend on where you maintain your
•
rupted period that includes an entire tax
How to figure the foreign housing exclu-
economic, family, and personal ties.
year, or
sion and the foreign housing deduction.
•
A U.S. citizen or a U.S. resident alien who
Example 1. You are employed on an off-
is physically present in a foreign country or
shore oil rig in the territorial waters of a foreign
Useful Items
countries for at least 330 full days during
country and work a 28-day on/28-day off sched-
You may want to see:
any period of 12 consecutive months.
ule. You return to your family residence in the
United States during your off periods. You are
Publication
See Publication 519 to find out if you qualify
considered to have an abode in the United
as a U.S. resident alien for tax purposes and
States and do not satisfy the tax home test in the
519
U.S. Tax Guide for Aliens
whether you keep that alien status when you
foreign country. You cannot claim either of the
596
Earned Income Credit
temporarily work abroad.
exclusions or the housing deduction.
Chapter 4 Foreign Earned Income and Housing: Exclusion – Deduction
Page 11
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Financial
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11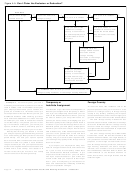 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26 27
27 28
28 29
29 30
30 31
31 32
32 33
33 34
34 35
35 36
36 37
37 38
38 39
39 40
40 41
41 42
42 43
43 44
44








