Publication 926 - Household Employer'S Tax Guide - Internal Revenue Service - 2012 Page 3
ADVERTISEMENT
Example. You made an agreement with John Peters to
available for review upon notice by an authorized U.S.
Government official.
care for your lawn. John runs a lawn care business and
offers his services to the general public. He provides his
Two copies of Form I-9 are contained in the Handbook
own tools and supplies, and he hires and pays any helpers
for Employers (Form M-274) published by the USCIS.
he needs. Neither John nor his helpers are your household
Call the USCIS at 1-800-870-3676 to order the
employees.
Handbook for Employers; or you may download
the handbook at If you have
More information. More information about who is an em-
questions about the employment eligibility verification pro-
ployee is in Publication 15-A, Employer’s Supplemental
cess or other immigration-related employment matters,
Tax Guide.
contact the USCIS Office of Business Liaison at
1-800-357-2099.
Can Your Employee Legally
You also can visit the USCIS website at
to get Form I-9.
Work in the United States?
For more information, see Employee’s Social Security
It is unlawful for you knowingly to hire or continue
Number (SSN) in Publication 15 (Circular E), Employer’s
!
Tax Guide.
to employ an alien who cannot legally work in the
United States.
CAUTION
When you hire a household employee to work for you on
Do You Need To Pay
a regular basis, you and the employee must complete the
U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS) Form
Employment Taxes?
I-9, Employment Eligibility Verification. No later than the
first day of work, the employee must complete the em-
If you have a household employee, you may need to
ployee section of the form by providing certain required
withhold and pay social security and Medicare taxes, pay
information and attesting to his or her current work eligibil-
federal unemployment tax, or both. To find out,
ity status in the United States. You must complete the
read Table 1.
employer section by examining documents presented by
You do not need to withhold federal income tax from
the employee as evidence of his or her identity and em-
your household employee’s wages. But if your employee
ployment eligibility. Acceptable documents to establish
asks you to withhold it, you can. See Do You Need To
identity and employment eligibility are listed on Form I-9.
Withhold Federal Income Tax, later.
You should keep the completed Form I-9 in your own
records. Do not submit it to the IRS, the USCIS, or any
If you need to pay social security, Medicare, or federal
other government or other entity. The form must be kept
unemployment tax or choose to withhold federal income
Table 1. Do You Need To Pay Employment Taxes?
IF you ...
THEN you need to ...
A–
Pay cash wages of $1,800 or more in 2012 to any one Withhold and pay social security and Medicare taxes.
household employee.
•
The taxes are 13.3% of cash wages.
Do not count wages you pay to—
•
Your employee’s share is 5.65%.
•
(You can choose to pay it yourself and not
Your spouse,
•
withhold it.)
Your child under the age of 21,
•
•
Your share is 7.65%.
Your parent (see Social Security and Medicare
Taxes, later, for an exception), or
•
Any employee under the age of 18 at any time in
2012 (see Social Security and Medicare Taxes,
later, for an exception).
B–
Pay total cash wages of $1,000 or more in any
Pay federal unemployment tax.
calendar quarter of 2011 or 2012 to household
•
The tax is 0.6% of cash wages.
employees.
•
Wages over $7,000 a year per employee are not
Do not count wages you pay to—
taxed.
•
•
Your spouse,
You also may owe state unemployment tax.
•
Your child under the age of 21, or
•
Your parent.
Note. If neither A nor B above applies, you do not need to pay any federal employment taxes. But you may still need to
pay state employment taxes.
Publication 926 (March 2012)
Page 3
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Financial
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13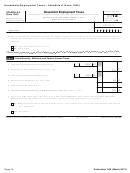 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20








