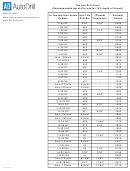
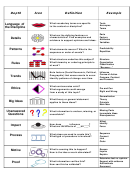
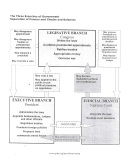
Structure And Bonding Chart Page 2
ADVERTISEMENT
Explain why thermosetting polymers don’t melt when heated, but
thermosoftening do.
Describe the sizes of nanoparticles in nm.
List uses of nanoparticles due to the high surface area to volume ratio.
C2.3 Atomic Structure, Analysis and Quantitative Chemistry.
Can you…?
Recall the masses and charges of protons, neutrons and electrons
Remember that protons + neutrons = mass number
Define the word isotope.
Recall that the relative atomic mass of an element (Ar) compares the mass of
atoms of the element with the 12C isotope. It is an average value for the
isotopes of the element.
The relative formula mass (Mr) of a compound is the sum of the relative
atomic masses of the atoms in the numbers shown in the formula.
State that the relative formula mass of a substance, in grams, is known as one
mole of that substance
Describe the benefits of using instrumental methods to detect and ID
elements and compounds
Describe how chemical analysis like paper chromatography allows us to ID
additives in food – like artificial colours.
Describe how gas chromatography linked to mass spectroscopy (GC-MS)
works and how it IDs the Mr of substances
Calculate the percentage of an element within a compound
[HT] Calculate the empirical formula of a compound from its mass or
percentages.
[HT] Calculate the masses of reactants or products from balanced symbol
equations
Calculate the percentage yield from a chemical reaction
Calculate the atom economy of a reaction
Represent a reversible reaction using a word equation
C2.4 Rates of Reactions
Can you…?
Look at a graph and work out the rate of reaction from products forming.
Describe the changing rate of a reaction by looking at a graph
Evaluate the advantages and disadvantages of using catalysts in industry
Can you calculate the rate of a reaction using this:
Rate of reaction = Amount of reactant used/time
Name 5 factors that would affect the rate of a reaction
Describe collision theory in terms of particles
and energy
Recall the name of the energy needed to be overcome to start a reaction
Explain how each factor would affect the rate of reaction using collision theory
State what a catalyst is and what it does
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4