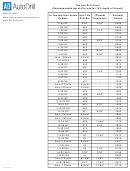
Structure And Bonding Chart
ADVERTISEMENT
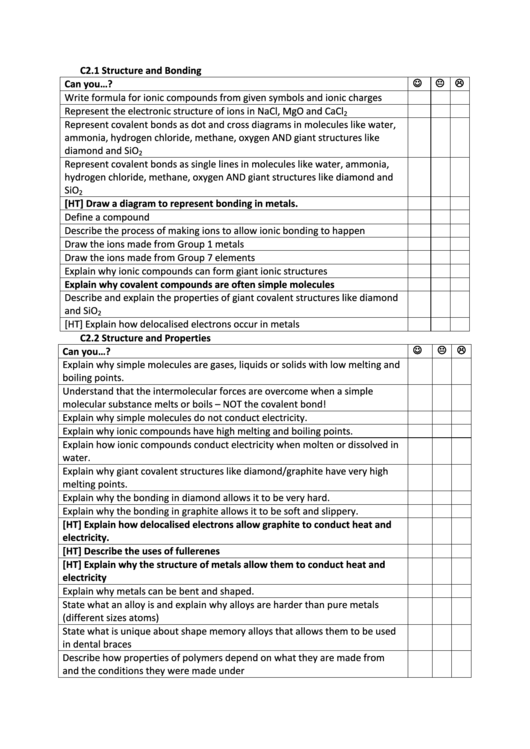
C2.1 Structure and Bonding
Can you…?
Write formula for ionic compounds from given symbols and ionic charges
Represent the electronic structure of ions in NaCl, MgO and CaCl
2
Represent covalent bonds as dot and cross diagrams in molecules like water,
ammonia, hydrogen chloride, methane, oxygen AND giant structures like
diamond and SiO
2
Represent covalent bonds as single lines in molecules like water, ammonia,
hydrogen chloride, methane, oxygen AND giant structures like diamond and
SiO
2
[HT] Draw a diagram to represent bonding in metals.
Define a compound
Describe the process of making ions to allow ionic bonding to happen
Draw the ions made from Group 1 metals
Draw the ions made from Group 7 elements
Explain why ionic compounds can form giant ionic structures
Explain why covalent compounds are often simple molecules
Describe and explain the properties of giant covalent structures like diamond
and SiO
2
[HT] Explain how delocalised electrons occur in metals
C2.2 Structure and Properties
Can you…?
Explain why simple molecules are gases, liquids or solids with low melting and
boiling points.
Understand that the intermolecular forces are overcome when a simple
molecular substance melts or boils – NOT the covalent bond!
Explain why simple molecules do not conduct electricity.
Explain why ionic compounds have high melting and boiling points.
Explain how ionic compounds conduct electricity when molten or dissolved in
water.
Explain why giant covalent structures like diamond/graphite have very high
melting points.
Explain why the bonding in diamond allows it to be very hard.
Explain why the bonding in graphite allows it to be soft and slippery.
[HT] Explain how delocalised electrons allow graphite to conduct heat and
electricity.
[HT] Describe the uses of fullerenes
[HT] Explain why the structure of metals allow them to conduct heat and
electricity
Explain why metals can be bent and shaped.
State what an alloy is and explain why alloys are harder than pure metals
(different sizes atoms)
State what is unique about shape memory alloys that allows them to be used
in dental braces
Describe how properties of polymers depend on what they are made from
and the conditions they were made under
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4