Electronic Structure Of The Atom Worksheet Page 4
ADVERTISEMENT
11. The electron configuration of an ion is determine in the same manner as that for an atom except that the number of
electron must be adjusted based on the charge of the ion. An atom with the same number of electron as an ion will have
the same electron configuration. From the above example, the carbon atom has six electrons and has an electron
configuration of C = [He]2s 2 2p 2 . A nitrogen +1 cation will also have the exact electron configuration N + = [He]2s 2 2p 2 .
Note that the nitrogen atom has an electron configuration of N = [He]2s 2 2p 3 but the +1 ion has one less electron, 6
instead of 7. Similarly, O +2 , F +3 , B -1 all have six electrons and therefore all have the electron configuration,
[He]2s 2 2p 2 . Complete the electron configuration for the following atoms.
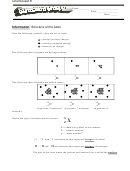
Atom
electron-configuration
Atom
electron-configuration
i.e. 32 Ge -4
1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s2 3d 10 4p 6
-1
34 Se
-3
+3
15 P
21 Sc
+2
-3
20 Ca
15 N
10.
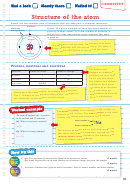
Orbital box diagrams are used to show the location of electrons in the outer shell. Inner (“core”) electrons are those
that correspond to the nearest noble gas and are not typically represented. So iron, which has an electron
2
6
configuration of [Ar] 4s
3d
would have an orbital box diagram that looks like
4s
3d
The presence of unpaired electrons will cause the species to be paramagnetic; if ALL the electrons are paired it is
said to be diamagnetic.
Write out the electron configurations for the following atoms and ions. Determine the number of unpaired electrons
in the ground state. (continue on back if needed)
+3
+2
+4
+2
22 Ti
25 Mn
15 P
65 Tb
78 Pt
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5