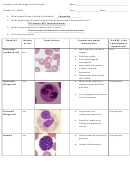
Unit 10 Review Key -Ocean Currents Page 3
ADVERTISEMENT
17. What are some climate effects of La Nina? North America experiences colder than normal weather. There are les
Typhoons in the Pacific and more Hurricanes in the Atlantic. Fish populations thrive off the coast of South
America due to increased upwelling.
18. How does El Nino affect upwelling and the fisheries off the coast of South America? Upwelling of cold deep
nutrient rich waters slows or stops during an El Nino. This cuts off the nutrients necessary to maintain the food
web along the coast of South America. As a result fish populations crash as do populations of other species that
rely on fish such as seabirds.
Deep Water Currents
19. What is the primary force that drives deep water currents? They are driven by differences in density that are
caused by differences in temperature and salinity. This is called thermalhaline circulation.
20. What two factors affect thermohaline circulation? temperature and salinity
21. What is the Global Conveyor Belt? It is the global circulation pattern of deep ocean currents.
22. Where does it start? In the North Atlantic when cold salty dense water sinks and begins to move south.
23. How does the Global Conveyor Belt and ocean currents affect atmospheric carbon dioxide? The oceans are a
carbon sink. The Global Conveyor Belt carries dissolved carbon dioxide and carbon from plankton away from the
atmosphere and sequesters it in the deep oceans for thousands of years.
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3