Thermodynamics Formulas
ADVERTISEMENT
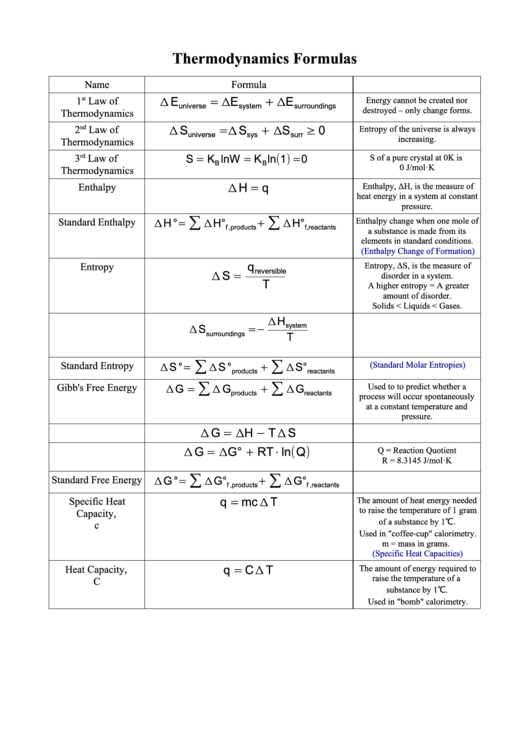
Thermodynamics Formulas
Name
Formula
st
Δ E
= Δ E
Energy cannot be created nor
1
Law of
+ ΔE
universe
system
surroundings
destroyed – only change forms.
Thermodynamics
Δ S
= Δ S
≥ 0
2
nd
Law of
Entropy of the universe is always
+ ΔS
universe
sys
surr
increasing.
Thermodynamics
3
rd
Law of
S = K
lnW = K
ln(1) = 0
S of a pure crystal at 0K is
B
B
0 J/mol·K
Thermodynamics
Enthalpy
Δ H = q
Enthalpy, ΔH, is the measure of
heat energy in a system at constant
pressure.
∑
∑
Enthalpy change when one mole of
Standard Enthalpy
Δ H ° =
Δ H°
Δ H°
+
f ,products
f , reactants
a substance is made from its
elements in standard conditions.
(Enthalpy Change of Formation)
Entropy
q
Entropy, ΔS, is the measure of
reversible
Δ S =
disorder in a system.
T
A higher entropy = A greater
amount of disorder.
Solids < Liquids < Gases.
Δ H
system
Δ S
= −
surroundings
T
∑
∑
Standard Entropy
(Standard Molar Entropies)
Δ S ° =
Δ S °
Δ S°
+
products
reactants
∑
∑
Used to to predict whether a
Gibb's Free Energy
Δ G =
Δ G
Δ G
+
products
reactants
process will occur spontaneously
at a constant temperature and
pressure.
Δ G = ΔH − T Δ S
Δ G = ΔG° + RT ⋅ln(Q)
Q = Reaction Quotient
R = 8.3145 J/mol·K
∑
∑
Standard Free Energy
Δ G ° =
Δ G°
ΔG°
+
f ,products
f , reactants
q = mc Δ T
Specific Heat
The amount of heat energy needed
to raise the temperature of 1 gram
Capacity,
of a substance by 1℃.
c
Used in "coffee-cup" calorimetry.
m = mass in grams.
(Specific Heat Capacities)
Heat Capacity,
q = C Δ T
The amount of energy required to
raise the temperature of a
C
substance by 1℃.
Used in "bomb" calorimetry.
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1