Ph Chart - Chemistry Reference Sheet
ADVERTISEMENT
At 25°C, K
= 1.0×10
-14
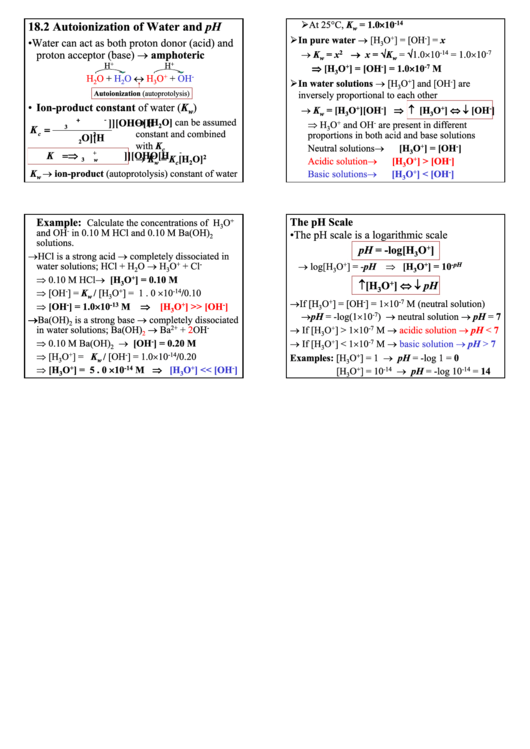
18.2 Autoionization of Water and pH
w
In pure water → [H
O
+
] = [OH
-
] = x
• Water can act as both proton donor (acid) and
3
proton acceptor (base) → amphoteric
→ K
→ x = √K
= √1.0×10
= x
2
-14
= 1.0×10
-7
w
w
H
+
H
+
⇒ [H
O
+
] = [OH
-
] = 1.0×10
-7
M
3
↔
+
-
H
O
+
H
O
H
O
+
OH
In water solutions → [H
O
+
] and [OH
-
] are
2
2
3
3
Autoionization (autoprotolysis)
inversely proportional to each other
• Ion-product constant of water (K
)
→ K
] ⇒ ↑[H
] ⇔ ↓[OH
= [H
O
+
][OH
-
O
+
-
]
w
w
3
3
+
→ [H
-
O] can be assumed
[H
O
][OH
]
⇒ H
O
+
and OH
-
are present in different
2
=
K
3
3
constant and combined
proportions in both acid and base solutions
c
2
[H
O]
2
with K
Neutral solutions →
[H
O
+
] = [OH
-
]
c
+
3
⇒
=
-
K
[H
O
][OH
]
→ K
= K
[H
O]
2
Acidic solution →
[H
O
+
] > [OH
-
]
w
3
w
c
2
3
→ ion-product (autoprotolysis) constant of water
→
K
Basic solutions
[H
O
+
] < [OH
-
]
w
3
The pH Scale
Example:
Calculate the concentrations of H
O
+
3
and OH
-
in 0.10 M HCl and 0.10 M Ba(OH)
• The pH scale is a logarithmic scale
2
solutions.
pH = -log[H
O
+
]
→HCl is a strong acid → completely dissociated in
3
O → H
→ log[H
] = -pH ⇒ [H
water solutions; HCl + H
O
+
+ Cl
-
O
+
O
+
] = 10
-pH
2
3
3
3
⇒ 0.10 M HCl → [H
+
O
] = 0.10 M
↑[H
] ⇔ ↓pH
O
+
3
3
⇒ [OH
-
] = K
/ [H
O
+
] = 1.0×10
-14
/0.10
w
3
→If [H
O
+
] = [OH
-
] = 1×10
-7
M (neutral solution)
⇒ [OH
M ⇒
-
] = 1.0×10
-13
[H
O
+
] >> [OH
-
]
3
3
→pH = -log(1×10
) → neutral solution → pH = 7
-7
→Ba(OH)
is a strong base → completely dissociated
2
→ Ba
→ If [H
M →
acidic solution → pH < 7
in water solutions; Ba(OH)
2+
+ 2OH
-
O
+
] > 1×10
-7
2
3
⇒ 0.10 M Ba(OH)
→ [OH
→ If [H
M →
basic solution → pH > 7
-
] = 0.20 M
O
+
] < 1×10
-7
2
3
⇒ [H
O
+
] = K
/ [OH
-
] = 1.0×10
-14
/0.20
] = 1 → pH = -log 1 = 0
Examples: [H
O
+
3
w
3
⇒ [H
M ⇒
O
+
] = 5.0×10
-14
[H
O
+
] << [OH
-
]
→ pH = -log 10
[H
O
+
] = 10
-14
-14
= 14
3
3
3
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3