Discovery Activity 12: Speed And Stopping Distance
ADVERTISEMENT
Discovery Activity 12: Speed and Stopping Distance
Suppose while driving you see the brake lights of the car in front of you come on. If you assume
the car ahead is going to stop and your brakes must be applied, then how far will your car travel
before it comes to a stop? In other words, what is the stopping distance from the moment your
brain receives the signal to brake until the car is no longer moving?
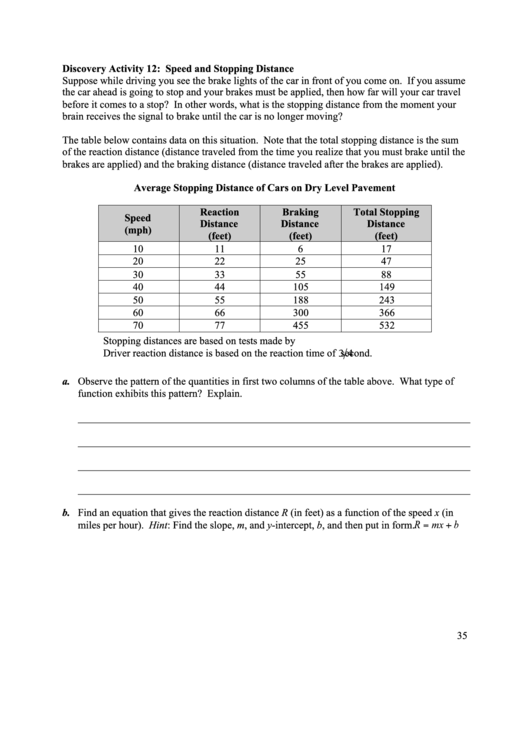
The table below contains data on this situation. Note that the total stopping distance is the sum
of the reaction distance (distance traveled from the time you realize that you must brake until the
brakes are applied) and the braking distance (distance traveled after the brakes are applied).
Average Stopping Distance of Cars on Dry Level Pavement
Reaction
Braking
Total Stopping
Speed
Distance
Distance
Distance
(mph)
(feet)
(feet)
(feet)
10
11
6
17
20
22
25
47
30
33
55
88
40
44
105
149
50
55
188
243
60
66
300
366
70
77
455
532
Stopping distances are based on tests made by U.S. Bureau of Public Roads.
Driver reaction distance is based on the reaction time of
second.
a. Observe the pattern of the quantities in first two columns of the table above. What type of
function exhibits this pattern? Explain.
___________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________
b. Find an equation that gives the reaction distance R (in feet) as a function of the speed x (in
miles per hour). Hint: Find the slope, m, and y-intercept, b, and then put in form
.
35
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3