German Personal Pronouns
ADVERTISEMENT
Personal Pronouns
Preliminary Notes - For Lectures - Please Watch for errors
Personal pronouns are words that are used to take the place of nouns. After the speaker has made reference to a noun, then a
pronoun can be substituted for that noun from then on in the discourse. A personal pronoun carries somewhat different
information from the noun it replace.s The most important feature of a personal pronouns is that it indicates the perspective of
the speaker. Here are some examples in English of perspective. The noun we will be replacing is “John”.
“John is a nice man.”
If the speaker is talking to someone about John, then there are three people involved in the perspective: the speaker, the listener,
and a third person “John”. We can replace “John” with “he”.
“He is a nice man.”
The perspective of the speaker in relationship to John is remote. John is a third party not involved in the conversation. The
perspective of the pronoun “he” shows “about”. This is called “third person”.
If John is being addressed directly, then the perspective of the speaker is one in which John and the speaker are in contact with
each other. There are only two people involved in the situation, and John is the second person. We replace “John” with “you”.
“You are a nice man.”
The pronoun “you” is called second person. The perspective of the pronoun “you” shows “to”.
If the noun being replaced is also the name of the speaker, then a pronoun is used to indicate that John and the speaker are one
in the same:
"I am a nice man."
"I" is used to replace "John". There is only one person involved in this act, and John is it. This is called first person. The
perspective of "first person" is "self".
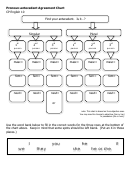
The following is a chart of the above information:
I
1st person
the pronoun indicates the noun is equal to the speaker
"self"
you
2nd person
the pronoun indicates the noun is being addressed
"to"
he
3rd person
the pronoun indicates the noun is being referred to
"about"
We can make a further distinction in the third person, one of gender. If the noun is feminine, we replace it with "she", and if
the noun is neuter, we replace it with "it". In German, all nouns, regardless of whether they are people or not, have gender.
Each noun must take a gender appropriate pronoun. Example: the word for "table" (Tisch) in German is masculine. The
pronoun to replace "table" must also be masculine. The German word for "child" (Kind) is neuter and must be replaced with a
neuter pronoun.
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3